|
|
[ < ]
[ Help Home ]
[ > ]
Organizing Your Data: User Space
- My Data

- Overview

"My data" just looks like user's disk space on web. While guest users have to upload files from local disk or paste
sequences in
the text area each time, every registered user has a user space to store sequences for subsequent analysis.
- It is convenient to choose saved files for different analysis.
- Users can continue doing their work without space limit, i.e. they can do their analysis in any
place
using different computers, for WebLab preserves all the data they need on the server.
- Also, users can
share their data with appointed collaborators.
- Basic Operation

We provide some basic operations for users' files, including directory operations, file upload, modify, delete, share
and operations on comment and tag.
- Directory Operation

Users can make directories to store data hierarchically, which is convenient for users who have large amount of data
and
analysis results to manage. Users can also delete, rename or move these directories.
- File Upload

There are several ways to upload files. For uploaded files, users can rename, move or delete them as well as change
associated file format.
- Paste sequences into text box
- Upload files from local disk
- Get data from the resource module integrated in WebLab
Note: WebLab has an internal data format vocabulary which defines various data types used in biomedicine domain.
Please try to specify proper data format to the uploading data file, because many default manipulations on data are dependent on the data format.
Users can also choose to change the data format in "My Data" later.
-
Data Operation

For non-binary data files, users can view the content by clicking the file name.
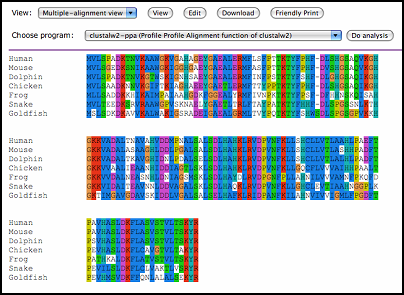
For some special data format, WebLab provides users a more intuitive view, which is the render mechanism in WebLab.
Renders for some familiar types are implemented now, including ClustalW, pairwise alignment output, KOBAS
result, Prints and Prosite database search result. User can select view type
to have a better understand of the result.
 [+] Enlarge the image
[+] Enlarge the image
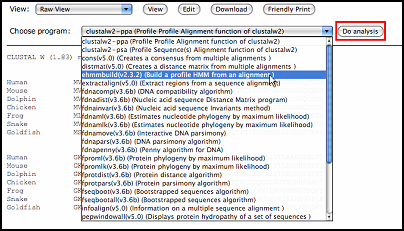
User can edit data or print data file directly by clicking the corresponding buttons.
By clicking "do analysis" button, user can choose program from the program list to do further analysis.
Note: The system will list all the available programs according to the appointed data
format. Therefore, different data format will have different program list.
 [+] Enlarge the image
[+] Enlarge the image
-

-

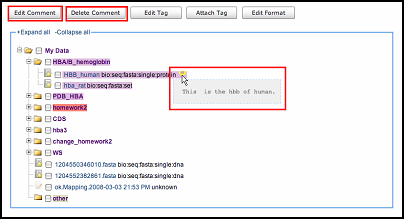
Comment is the user's description of the file. It helps users to understand the content in a short time to
improve
work efficiency. Users can add, edit or delete comments on file to make it more understandable.
Then, when you put your mouse over the yellow icon, you will find the short description on your data.
 [+] Enlarge the
image
[+] Enlarge the
image
-
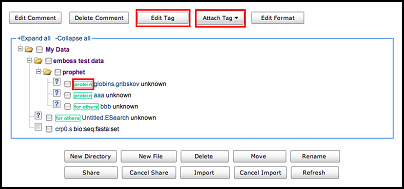
Tag

In addition to be organized as classical hierarchical ˇ°tree viewˇ±, items in "my data" could also be browsed as different views through customized ˇ°tagˇ±.
 [+] Enlarge the
image
[+] Enlarge the
image
Users can create or edit tags by clicking "edit tag" button and attach the customized tag to files by clicking "attach tag" button.
Note: "My data", "my literature" and "my metapackage" share one common tag system.
 [+] Enlarge the
image
[+] Enlarge the
image
- Share

All the items in "my data", "my literature" and "my metapackage" can be shared to your research collaborators. Here is the exhaustive introduction.
- My Literature

- Overview

WebLab provides a "my literature" for users to manage their literatures. Besides the functions in "my data",
WebLab also provides comprehensive supports by allowing full-text searching and inter-operation with citation managers such as EndNote and Pubmed.
- Upload Literature

Users can upload literatures they concerned to appointed directory. Now we accept
.txt,
.pdf and
.doc format of literature. Besides, we support batch upload. User can upload at most
10
English literatures each time, each of which is no more than
10M.
 [+] Enlarge the image
[+] Enlarge the image
- Citation

Besides literature file, WebLab also allows users to add citation information for each literature.
Citation information supplies users sufficient details for each literature. Users can search literature through citation information. More importantly, all the citation information can be exported as famous citation format such as
Endnote import format, bibtex and so on.
Now WebLab provides "fetch citation", "delete citation", "delete citation" and "export citation" functions in "my literature".
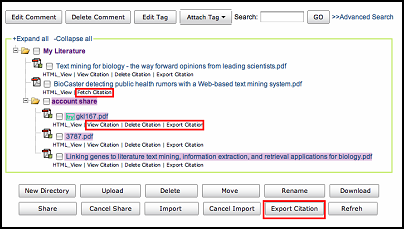 [+] Enlarge the image
[+] Enlarge the image
For literature without citation information, users can fetch citation from Pubmed providing pubmedID or literature title.
WebLab will fetch and then store the citation information in intermediate format.
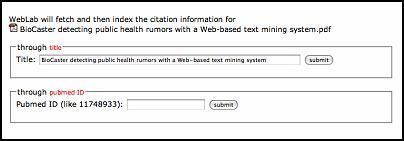 [+] Enlarge the image
[+] Enlarge the image
Users can glimpse the citation through "view citation".
Note: WebLab only presents title, authors, journal name, publish date, volume, issue, page, abstract and pubmedID information rather than all the citation information.
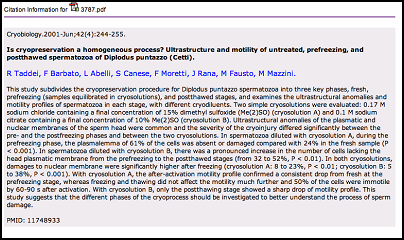 [+] Enlarge the image
[+] Enlarge the image
Citation information can be exported in single(button under each literature item) or batch(button under whole literature space) mode. Users can select the exported format. Now WebLab support
Endnote, BibTeX, ADS reference format, ISI format, RIS format and Word 2007 bibliography format.
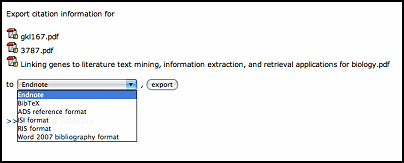 [+] Enlarge the image
[+] Enlarge the image
- Indexing and Searching

During literature uploading process, WebLab will extract literature content and build the index for full text information.
Analogously, partial citation information (title, authors, journals, publish date)will be extracted and built index during the citation fetching process.
Now, WebLab uses Lucene
as our information index and retrieval library.
Note: Sometimes, WebLab can not extract full text content or citation information, so index can not be built (WebLab will try to
provide error reason). For example, WebLab can't build index for decrypt PDF file.
WebLab uses different icons to record index status for literatures: pink color means this part of literature can not be indexed, either full text or citation information.

For literatures whose index have been successfully built, users can search the corresponding information through simple search and advanced search provided by WebLab.
Simple search only provides key words search for full text content.
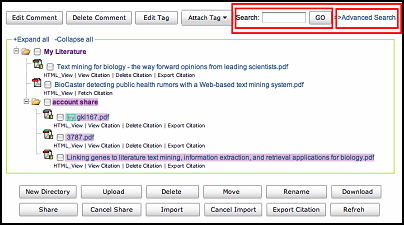 [+] Enlarge the
image
[+] Enlarge the
image
While for the advanced search, user can compose complex query to do the search for both full text and citation information.
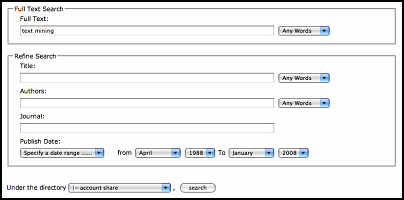 [+] Enlarge the
image
[+] Enlarge the
image
The result of search is as follow. The search keywords will be highlighted. The score for each literature
is the matching score. Literature which matches the search query better will be sorted in front.
 [+] Enlarge the
image
[+] Enlarge the
image
- HTML Preview

For every literature stored in "My Literature", WebLab provides html preview function in order to
give an online snapshot of the content of every literature.
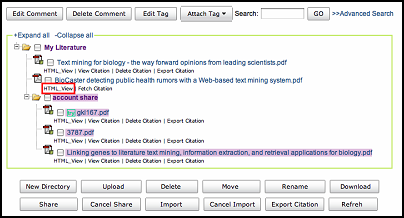 [+] Enlarge the
image
[+] Enlarge the
image
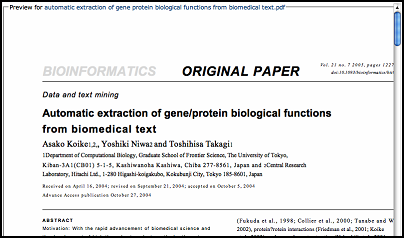 [+] Enlarge the
image
[+] Enlarge the
image
- My Meta Package

[ < ]
[ Help Home ]
[ > ]
|

